|

Biome boundary
(borealbiome.zip 77 KB)
The boreal biome was delineated using the World Wildlife Fund terrestrial ecoregions map. This map was modified to add ecoregions of temperate coniferous and mixed forests characterized by similar seasonality and presence of winter snow cover. Also forested areas of forest-steppe ecoregions within continental parts of North America and Asia, along with forest-tundra transitional ecoregions, were included in the boreal biome. Due to data limitations, a small portion of the boreal forest biome (Iceland and areas greater than 70° latitude in Siberia) was not processed. For the purpose of the sampling analysis, the biome was partitioned into a sampling frame consisting of square blocks 18.5 km per side. The shapefile contains the sampling frame boundary for the boreal biome.
Data format: ESRI shape
Projection: Lat/Long
MODIS-derived data
MODIS data alone are inadequate for accurate change area estimation because most forest clearing occurs at sub-MODIS pixel scales. For forest cover and forest cover loss area calculation please use the calibrated products at 18.5 km resolution.
Tree canopy density product
(boreal_vcf_500m.zip 62.5 MB)
The MODIS-based Vegetation Continuous Field (VCF) layers provide estimates of global and regional vegetation cover for the study of biogeochemical cycles, ecosystem assessment, and land management. The VCF product depicts global sub-pixel estimates of vegetative components (tree cover, herbaceous cover, and bare cover) at 500m. The current dataset is a subset of the year 2000 VCF Collection 4 tree canopy cover layer for the boreal biome.
Data format: GeoTiff. 8-bit unsigned integer data.
Pixel size: 463.3127m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
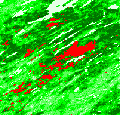
Forest cover loss hotspot map (2000-2005)
(boreal_hotspots_500m.zip 1.2 MB)
Biome-wide forest cover loss hotspot maps were created using annual MODIS imagery from 2000 to 2005. The regression tree algorithm related forest cover loss training data to the MODIS inputs, resulting in a per pixel 5-year change fraction map. We applied a 5% change fraction threshold to produce a per pixel forest change hotspot map. These data represent areas of intensive forest cover clearing.
Data format: GeoTiff. 8-bit unsigned integer data.
Pixel size: 463.3127m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
Annual forest cover loss hotspot maps (2000-2005)
(boreal_hotspots_years_500m.zip 1.6 MB)
To analyze temporal trends, we disaggregated the change depicted by the 5-year forest loss hotspot map by identifying the year of maximum forest cover loss within the set of 5 annual intervals (2000-2001, 01-02, 02-03, 03-04 and 04-05). Taking into account the fact that the most important MODIS inputs for change detection within the regression tree models were for the growing season (June-August), we expected that change occurring during fall and winter might only be detected during the subsequent growing season. Hence, results reflect annual intervals from August of the preceding year to August of the following year.
Data format: GeoTiff. 8-bit unsigned integer data.
Pixel size: 463.3127m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
Forest cover loss factors within 5-years forest cover loss hotspot map (2000-2005)
(boreal_hotspots_type_500m.zip 1.3 MB)
The analysis of forest cover loss factors was based on a decision tree classification. The objective was to discern the cause of the cleared forest cover per MODIS pixel. The classification results include two categories: burned forest areas and forest cover loss hotspots attributed to other disturbance factors (logging, insect outbreaks, blowdowns, etc.) within the 5-year change hotspot map.
Data format: GeoTiff. 8-bit unsigned integer data.
Pixel size: 463.3127m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
Landsat-calibrated data
Forest cover for year 2000
(boreal_forest_20km.zip 76 KB)
This dataset represents forest cover extent for the biome for year 2000. Forests were defined as areas with tree canopy cover greater than 25%. The Landsat-analyzed sample block classification results were used to calibrate biome-wide MODIS-derived forest extent. The relationship between Landsat-based forest cover area and mean VCF tree canopy density per sample block 18.5 km per side was used to derive forest extent for year 2000. A simple linear regression (no intercept) model was used with mean VCF tree canopy density per block as the independent variable.
Data format: GeoTiff. 32-bit data.
Pixel size: 18532.508m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
Forest cover loss 2000-2005
(boreal_change_20km.zip 57 KB)
This dataset represents 2000-2005 gross forest cover loss for the biome. A separate regression estimator (i.e. separate regression models and parameter estimates allowed for each stratum) and post-stratification were employed to estimate Landsat-calibrated forest cover loss area. For sample blocks with intensive change a simple linear regression model was applied using the proportion of area within the sample block classified as MODIS-derived forest loss as the auxiliary variable. For low-change blocks post-stratification based on VCF tree canopy cover and road density data was implemented to partition blocks into areas of nearly zero change and areas of some change. The forest cover loss area estimates were then constructed from the sample mean Landsat-derived clearing within post-strata.
Data format: GeoTiff. 32-bit data.
Pixel size: 18532.508m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
Forest cover loss due to wildfires 2000-2005
(boreal_fire_change_20km.zip 52 KB)
This dataset represents 2000-2005 gross forest cover loss due to wildfires for the biome. A separate regression estimator (i.e. separate regression models and parameter estimates allowed for each stratum) and post-stratification were employed to estimate Landsat-calibrated forest cover loss area. For sample blocks with intensive change a simple linear regression model was applied using the proportion of area within the sample block classified as MODIS-derived forest loss as the auxiliary variable. For low-change blocks post-stratification based on VCF tree canopy cover and road density data was implemented to partition blocks into areas of nearly zero change and areas of some change. The forest cover loss area estimates were then constructed from the sample mean Landsat-derived clearing within post-strata.
Data format: GeoTiff. 32-bit data.
Pixel size: 18532.508m.
Projection: Sinusoidal.
Provided MODIS-derived data are available for use for valid scientific, conservation, and educational purposes as long as proper citations are used. We ask that you credit the Boreal Forest Monitoring data as follows:
Potapov P., Hansen M.C., Stehman S.V., Loveland T.R., Pittman K. (2008) Combining MODIS and Landsat imagery to estimate and map boreal forest cover loss. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(9), 3708-3719.
We ask that you credit the Vegetation Continuous Fields data as follows:
Hansen, M., DeFries R.S., Townshend J.R.G., Carroll M., Dimiceli C., Sohlberg R.A. (2003) Global Percent Tree Cover at a Spatial Resolution of 500 Meters: First Results of the MODIS Vegetation Continuous Fields Algorithm. Earth Interactions, Vol 7, No 10, pp 1-15.
For further information, please contact:
Dr. Matthew Hansen
Geographic Information Science Center of Excellence - SDSU
Phone: (605) 688-6848
Matthew.Hansen@sdstate.edu
Dr. Peter Potapov
Geographic Information Science Center of Excellence - SDSU
Phone: (605) 688-5814
Peter.Potapov@sdstate.edu
|